Over the past few decades, scientific research has shed light on the remarkable world within us – the microbiome. Comprising trillions of bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms, our gut microbiome plays a critical role in maintaining our overall health and wellbeing. Recent studies have highlighted a strong connection between the microbiome and various diseases, including obesity, diabetes, and autoimmune conditions. This blog post aims to unravel this intricate relationship, providing insights into the potential impact of a balanced gut ecosystem on our health and its implications for disease prevention and management.
Understanding the Microbiome
The human microbiome refers to the vast and diverse collection of microorganisms that inhabit our bodies, with the gut being one of the most significant hubs. This complex ecosystem plays a crucial role in digestion, metabolism, and the development of our immune system. An imbalanced or unhealthy gut microbiome can lead to various health issues, including those related to metabolic and immune function.
Microbiome and Obesity
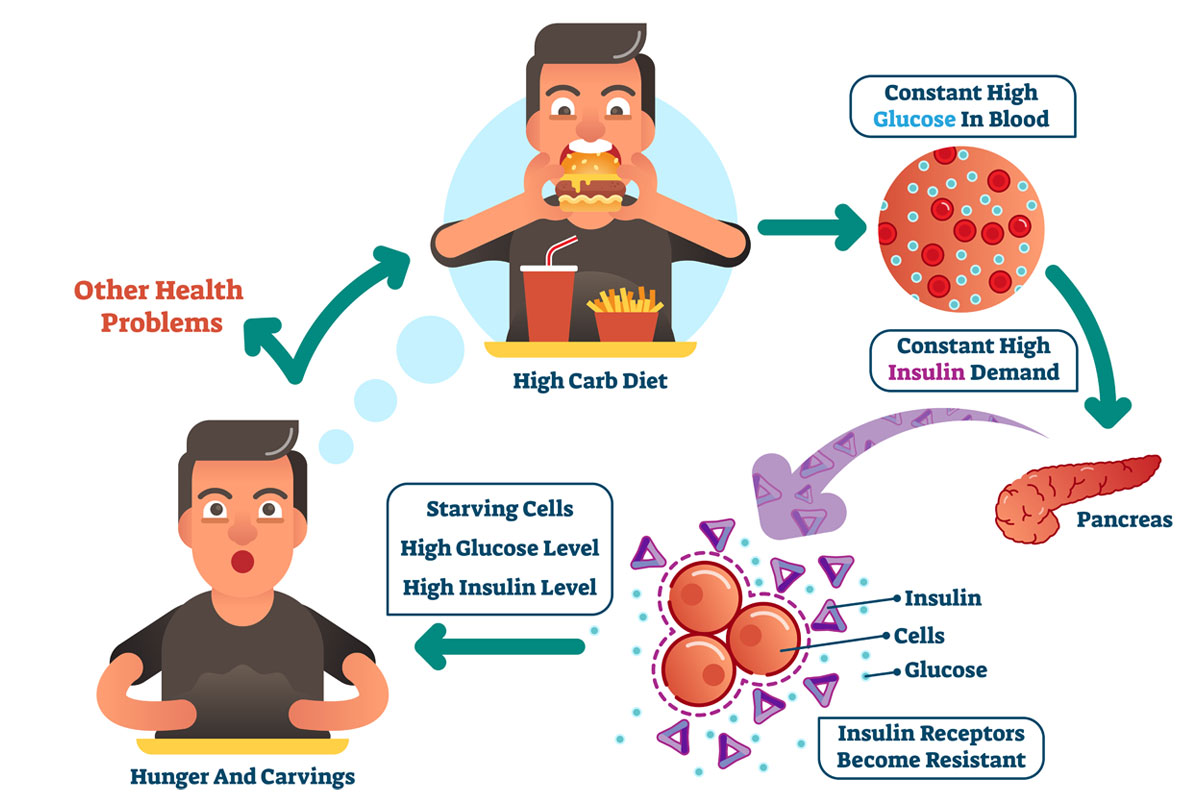
Obesity has become a global health concern, and researchers have found that the gut microbiome might have a role to play in its development. Studies have revealed that individuals with obesity tend to have a different composition of gut bacteria compared to those with a healthy weight. Certain species of bacteria found in the microbiome are associated with increased energy extraction from food, leading to weight gain. Moreover, an imbalanced microbiome can contribute to inflammation and insulin resistance, which are factors closely linked to obesity.
Microbiome and Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes, a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels, is another disease connected to the gut microbiome. Recent research suggests that specific bacteria in the gut can influence glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity. An imbalance in the gut microbiome may promote inflammation and disrupt the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar, contributing to the development and progression of diabetes.
Microbiome and Autoimmune Conditions
Autoimmune conditions occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues. Emerging evidence indicates that the gut microbiome could influence immune system development and function, making it a potential contributor to autoimmune diseases. Imbalances in the microbiome might trigger an inappropriate immune response, leading to the onset or exacerbation of conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and inflammatory bowel disease.
Maintaining a Healthy Microbiome
Fortunately, there are steps we can take to nurture a healthy gut microbiome and potentially reduce the risk of these diseases. Here are some practices to consider:
- Diet: A balanced and diverse diet rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and fermented foods can promote a diverse and thriving gut microbiome.
- Probiotics and Prebiotics: Probiotic foods and supplements contain beneficial live microorganisms that can bolster the gut microbiome, while prebiotic foods support the growth of beneficial bacteria.
- Antibiotic Use: Avoid unnecessary antibiotic use, as these medications can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can negatively impact the gut microbiome. Engage in stress-reducing activities like meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature.
The relationship between the gut microbiome and diseases like obesity, diabetes, and autoimmune conditions is an exciting area of ongoing research. While the exact mechanisms linking the microbiome to these diseases are still being unraveled, evidence suggests that maintaining a healthy gut ecosystem can have significant implications for our overall health. By embracing a lifestyle that promotes a diverse and balanced gut microbiome, we can take important steps towards preventing and managing these prevalent health conditions. Remember, a healthy gut can contribute to a healthier you!